Introduction to Linguistics
Linguistics is the study of a language system. And for a study purpose language is divided into different components. The component of linguistics is conventional because it also involves the analysis of language from language meaning. In this language, various building blocks of different types and sizes are combined to make up a language.
If you need more information or you have a question regarding Components of Linguistics, you can discuss it with our HearingSol healthcare professionals, just give us a call on +91-9327901950. We are always here to help you.
Traditionally linguists analyze human language by observing an interplay between meaning and sound. Therefore, It is nothing but the study of speech and non-speech sounds. Different types of sound brought together, they change their forms and do interesting things. It arranges words in a different order, Sometimes and starting and ending words are changed to adjust the meaning.
 The study of language also deals with how languages encode their relations between entities, properties, and other aspects of the world to convey, process, and assign meaning, moreover manage and resolve the ambiguity.
The study of language also deals with how languages encode their relations between entities, properties, and other aspects of the world to convey, process, and assign meaning, moreover manage and resolve the ambiguity.
While the study of semantics concerns itself with truth conditions, pragmatics deals with how situational context influences the meaning of production.
It traditionally analyzes human language by observing the interplay between sounds and also their meanings. There are various components of linguistics.
Components of linguistics:
There are mainly five components of any language they are phonemes, morphemes, lexemes, syntax, as well as context. Along with grammar, semantics, and pragmatics, these components work with each other in order to give meaningful communication among individuals and include various linguistic elements.
A component/parts or level of linguistics on the basis of their structure of language is categorized into a number of subfields.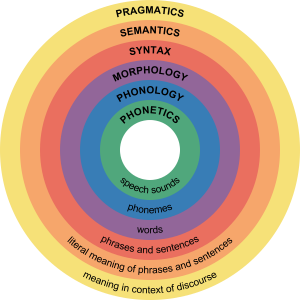
Phonology: It is the first component of linguistics and formed from Greek word phone. Phonology is a study of the structure or cognitive aspects of speech in language on the basis of speech units and also on pronunciation.
Phonetics: It is a study of speeches of sounds on the basis of their physical aspects.
Syntax: Many people get confused between grammar and syntax. It is a study of arrangement and order of words and also has a relationship between these hierarchical units.
Semantics: It is a study of the meaning conveyed in the words.
Pragmatics: A programmatic is the study of the functions in a language and also its context to use.
Morphology: The next component of linguistics is morphology. It is a study of structure or form of words in a specific language and also their classification. Therefore, it considers the principle of formation of words in a language.

Aside from language structure, there are a lot of perspectives on the language are represented in specialized or interdisciplinary branches.
Branches of linguistics
- Historical linguistics: It is the study of language changing over time.
- Sociolinguistics: It is the study of language according to the caste, gender, religion as well as occupation.
- Dialectology: The study of language according to the geographic distribution
- Pragmatics: The study of wherewith context provides the meaning
- Discourse analysis: The study of using the language
- Computational linguistics: The computational programs according to the model aspects of language
- Language acquisition: The study of acquiring and learning of language
- Psycholinguistics: The study of how people treat language
- Experimental Linguistics: The study of methods of linguistic description (phonetics, phonology, morphology, syntax, and semantics) based on evidence.
- Neurolinguistics: The study of whereby language affects the brain structure
- Lexicography: The compilation as well as the study of dictionaries with context, history, grammar, and pronunciation in memory
- Forensic Linguistics: The study of language as well as the law
- Corpus linguistics: The study of language with a collection of naturally occurring texts.
General principles of linguistic
The principle of Naturalness
Teaching must be done in a natural way. Our teaching must include only one or two basic skills .i.e. Listening and speaking. Further, there are two more skills, reading, and writing that comes automatically. Speaking will lead you to the writing, listening and reading. As the child gradually learns his mother tongue in the natural environment.
The principle of vocabulary
The main objective of teaching is to increase the vocabulary of the students. Vocabulary is mainly categorized into two parts, passive and active. The words which can be recognized and understood but not use in writing as well as spoken come in passive vocabulary. On the other side, the words which are easy to understand are considered as speaking and writing comes under active vocabulary.
The principle of Imitation
You can learn the language best by imitation because a good speech is the result of imitation of good models of speech. A teacher uses Audio- Video Aids for providing a good model of reading, writing, pronunciation, etc.
The principle of Habit formation
As every habit need practice e.g. Habits like singing and dancing needs practice. Likewise, languages also need practice. The habits lie in one’s personality deeply and reflect through speech behavior and thinking.
The principle of Practice
For bringing perfection in your language, practice is very important. The development of expression, International Journal of Technical Research (IJTR) grammar, vocabulary, pronunciation is based on the practice which should be continuous.
Grammar is the one which needs a lot of practice for knowing its rules deeply and in direct proportion. Fries recommended that eighty-four percents of time be devoted to practice and only fifteen percent to explanation and commentary.
The principle of contest and situation
Language is being taught to able the learners to make use of the words in their day-to-day life and its situations. You can make your learning easy if it is made up of real as well as suitable situations. The fundamental language which includes vocabulary, structure, and grammar should be taught by taking the help of structures and vocabulary that relates to real situations. You can create these situations by real objects, pictures, gestures, animations, etc.
The principle of mutuality
Language is fruitful if there is a mutual bond b/w teachers and learner. Both are essential in the teaching-learning process. The students must be co-operative to accept the matter wholeheartedly while learning the language. He should be ready for practicing and learning the foreign language as the teacher should be ready for providing the new language.
Read more…
