Autism is a mental condition, initiates from early childhood, characterized by an issue in communication and forming relationships with others. Its other name is Autism Spectrum Disorder(ASD) because of an array of symptoms.
Children suffering from autism might have repetitive, stereotypic body movements corresponding to rocking, pacing, or hand fluttering.
They can have uncommon responses to individuals, attachments to things, resistance to altering in their routines, or aggressive or self-injurious behavior.
If you need more information or you have a question regarding Autism affect the brain, you can discuss it with our HearingSol healthcare professionals, just give us a call on +91-9327901950. We are always here to help you.
Brain Study Finds Evidence – Autism Involves Too Many Synapses
A freshly printed brain-tissue study suggests that children with autism have a surplus of synapses or connections between brain cells. This is because of retardation within the traditional pruning method that happens throughout brain development said by the researchers.
The study team conjointly found that the medication rapamycin each restores traditional conjunction pruning and reduces autism-like behaviors They propose that sometimes an identical medication can be applied to treat autism after the diagnosis of a child or adult.
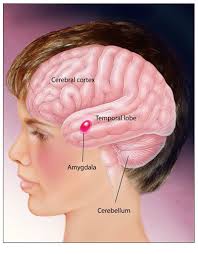
How does autism affect the brain?
Autism occurs in every region of the brain, not a particular part or corner. It has several causes and plenty of forms. However, regardless of that kind it adopts, it seems to influence the complete brain. It spreads throughout wiring and piping of the house, instead of simply a single room.
Each part of the brain uniquely reacts towards autism’s impact on cognition, emotion, and behavior.
Autistic brain vs Normal brain
- About 75% of the autistic brains differ very little in gene expression between the temporal and frontal lobes.
- People with the autistic brain has reduced cortical functional connectivity as compared to regular brain.
- The facial expression related connectivity and that of one’s self and the surroundings are very poor in brains with autism that affects computational components in mind.
Read more:
