A small earphone, or probe, is placed in your ear. The probe puts sounds into your ear and measures the sounds that come back. You don’t need to do or say anything during the test. Whoever the test can see the results on the monitor screen.
You can purchase the latest hearing aids at a fair price through HearingSol, If you need any assistance or you have a query regarding Otoacoustic Emissions Test (OAE) or Hearing Loss, feel free to call us at +91-9327901950. We are always here to help you.
What Is The Otoacoustic Emissions Test (OAE)?
The OAE (Otoacoustic Emissions Test) evaluation is often part of a newborn hearing screening program. Its purpose is to evaluate cochlear status and hair cell function. This test also is performed if the patient is sleeping because no behavioral response is required. This test record the sound of the ear and the sound which is recorded is produced itself by the ear.
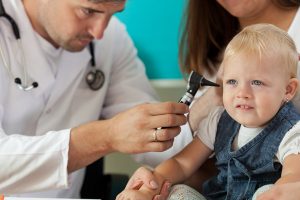
The OAE test can be performed in a few minutes. The hair cell response to the vibration sound, The sound which is produced is the OAE that is measured. It can help to detect sensorineural hearing loss and call attention to hearing disorders affecting the pathway to the inner ear. This test can be conducted by anyone who is trained to use the equipment and is skilled in working with children.
Otoacoustic Emissions Test Procedure
The test is performed with a portable handheld screening unit. A small probe is placed inside the child’s ear canal. This probe produces a low-volume sound stimulus into the ear. Your cochlea responds by producing an otoacoustic emission, sometimes described as an “echo,” that travels back through the middle ear to the ear canal and is analyzed by the screening unit.
Approximately 30 seconds, the result is displayed on the screening unit as a “pass” or a “refer.” Otoacoustic emissions screening can help to evaluate sensorineural hearing loss occurring in the cochlea. It also calls attention to hearing disorders affecting the pathway to the inner ear.
The probe which is inserted into the ear contains a loudspeaker that generates the sounds and a microphone that measures the resulting OAEs that are produced in the cochlea and transmitted by the middle ear into the outer ear canal. The resulting sound which is picked up by the microphone is now digitized and processed using the signal averaging methodology.
If you are obtaining an Otoacoustic Emissions you need an unobstructed outer ear canal, the absence of significant middle ear pathology, and functioning cochlear outer hair cells.
How OAE Screening Performed
- An initial screening of both ears on every child (birth to three years of age).
- Any ear not passing the initial (1st OAE) screening is screened again (2nd OAE) within approximately 2 weeks of the first screen.
- If the ear does not pass the 2nd OAE screen, the child must be evaluated by a health care provider to determine whether there is an outer ear or middle ear problem (blockage, fluid, structural anomaly, etc.) interfering with accurate completion of the OAE screening. Treatment or monitoring may be needed.
- Once the health care provider gives medical clearance, indicating that there are no conditions present that would impede an accurate screening, and Otoacoustic Emissions rescreen is conducted. If your ear was not able to pass the Otoacoustic Emissions rescreen, the child should be referred to a pediatric audiologist for a diagnostic evaluation. This referral is usually made by a health care provider in coordination with the Head Start program.
Two Types of Otoacoustic Emissions In Clinical Use:
- Transient otoacoustic emissions (TOAEs) or transient evoked otoacoustic emissions (TEOAEs) – Sounds emitted in response to an acoustic stimulus of very short duration; usually clicks but can be tone-bursts
- The second one is distortion product the otoacoustic emission – Sounds emitted in response to 2 simultaneous sound of different frequencies
Devices Used In OAE
In most of the clinics, the Otoacoustic Emissions devices are “screeners”. They typically check 5-10 frequencies and report whether the signal/noise ratio exceeds a preset limit, in which it indicates that the ear is a “pass”, or if not, a “refer”.
The “go/no-go” is a type of sound output often result and helpful in deciding whether there is any hearing problem or not — people who “pass” at all frequencies are not having anything seriously wrong with their inner ear. OAE’s are quick and not bothersome to patients.
Systems
The OAE elements pathway includes the sound source, the eardrum, ossicular chain, inner ear, and outer hair cells. The similar structures like before transmit sound coming out of the outer hair cells.
Otoacoustic Emissions can be affected by anything in the chain – -if the sound doesn’t get in or out — no OAE. If there is a resonance or filter between the sound source and microphone this will cause an altered frequency spectrum of OAEs (Grenner, 2012).
Thus, OAEs “reflect” a combination of the inner ear and external/middle ear function. People who have small ear canals (such as infants) are different than adults due to the difference in external and middle ear size.
Utility Used In OAE
The clinical sense of Otoacoustic Emissions is that they only occur in a normal cochlea with normal or near-normal hearing. If there is any kind of damage to the outer hair cells producing mild hearing loss, then OAEs are not evoked.
A rule of thumb is that OAEs are present if the hearing is 35 dB or better. Because OAEs are evoked by transient signals that have a wide frequency response, a broad region of the cochlea responds, providing information on the frequency range from 1000 Hz to 4000 Hz. OAE’s decline with age.
For any further queries, you can call on our toll-free number: +91-9327901950.
Email us: [email protected]
Our address: 211 Agarwal Tower H-6 Netaji Subhash Place Pitampura New Delhi 110034 India.

