Jaundice i.e. harsh enough to require a blood transfusion can also result in hearing loss. It is with the potential harm that high levels of bilirubin can affect the nerves of hearing.
Before understanding the relationship between Hyperbilirubinemia jaundice and hearing loss, it is important to know the core concept of Hyperbilirubinemia jaundice. So let’s begin with the introduction and continue our main topic.
You can purchase the latest hearing aids at a fair price through HearingSol, If you need more information or you have a query about Hyperbilirubinemia Jaundice Cause Hearing Loss, just give us a call on +91-9327901950. We are always here to help you.
What is Hyperbilirubinemia jaundice?
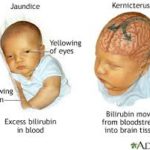
The Hyperbilirubinemia is a physical condition in which too much bilirubin founds in the blood. The bilirubin is formed when red blood cells break down into bilirubin, and the child is not able to get relief from bilirubin. It may build up in the blood, other tissues, and fluids of the baby’s body, known as hyperbilirubinemia because bilirubin produces a pigment or coloring. It causes a yellowing of the baby’s skin, eyes, and other tissues known as jaundice.
The relation between Hyperbilirubinemia jaundice and hearing loss
Introduction
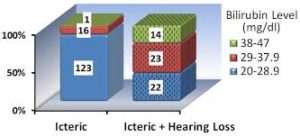
Now the question provokes our mind if Hyperbilirubinemia jaundice can lead to hearing loss. Based on our findings, neonatal hyperbilirubinemia can cause abnormalities in auditory evaluations, including behavioral audiometry. However, it seems that there is no clear and direct relationship between serum bilirubin levels and hearing thresholds. Therefore, behavioral hearing thresholds and hearing system impairment cannot be estimated solely based on maximum bilirubin levels at birth.
How Hyperbilirubinemia jaundice causes hearing loss
- Hearing loss and auditory dysfunction are well-recognized sequelae of hyperbilirubinemia.
- Bilirubin, at high levels, can damage auditory structures such as the brainstem auditory nuclei, inferior colliculi, spiral ganglion neurons, and auditory nerve fibers.
- The effect of hyperbilirubinemia on auditory dysfunction is generally dose-dependent, with greater dysfunction noted at higher total serum bilirubin (TSB) levels.
- The auditory pathway is the most sensitive part of the central nervous system to bilirubin-induced toxicity. Permanent sequelae may result from only moderately elevated total serum/plasma bilirubin levels. The damage to the auditory system occurs primarily within the brainstem and cranial nerve VIII and manifests clinically as an auditory neuropathy spectrum disorder.
Conclusion
The current condition showed that increase blood bilirubin levels in the infant period can be considered as one of hearing loss.
Thus, hyperbilirubinemia jaundice can lead to hearing loss as it has been cleared from the above points. As it adversely affects the nervous system and auditory system of the children.
Read More –